Build with kadena-cli
The Kadena command-line interface (kadena-cli) provides direct access to the Kadena blockchain and to commands that help you create, test, deploy, and manage applications for the Kadena network.
You can use the Kadena command-line interface to perform tasks interactively or in scripts and automated workflows that don't allow interactive input.
The Kadena CLI has one primary entry point—the kadena parent command.
By providing a single entry point for performing a wide range of tasks, the Kadena CLI integrates naturally into the typical development workflow.
With commands designed specifically for building, testing, and managing Kadena-based applications, you can focus on building innovative applications using familiar tools.
Before you begin
Before you use the Kadena command-line interface, verify the following basic requirements:
-
You have
node, version 18 or later, installed.Run
node --versionto verify the version you are running. -
You have the
pnpmpackage manager installed.Depending on your development environment, you can install pnpm using a standalone script or using a package manager. For example, you can run the command
brew install pnpmornpm install --global pnpmto install pnpm on your local computer. For more information about installing pnpm on different operating systems, see Installation.Run
pnpm --versionto verify that you have pnpm installed and the version you are running.
Install
The Kadena CLI is packaged in a TypeScript library that you can install using a package manager such as npm or pnpm.
To install globally using npm package manager, run the following command:
npm install -g @kadena/kadena-clinpm install -g @kadena/kadena-cliTo install globally using pnpm package manager, run the following command:
pnpm install -g @kadena/kadena-clipnpm install -g @kadena/kadena-cliTo verify the package is installed and display usage information, type kadena and press Return:
kadenakadenaTo see the version of the package you have installed, run the following command:
kadena versionkadena versionGet started
The kadena-cli package is designed to streamline the development workflow with commands that provide direct
access to everything you need to build on and interact with Kadena networks.
Whether you're doing local development, deploying an application on the test network, or managing your accounts and keys on the Kadena main network, you can use the kadena-cli commands to complete tasks without leaving your development environment.
The following diagram provides an overview of the kadena command-line interface:
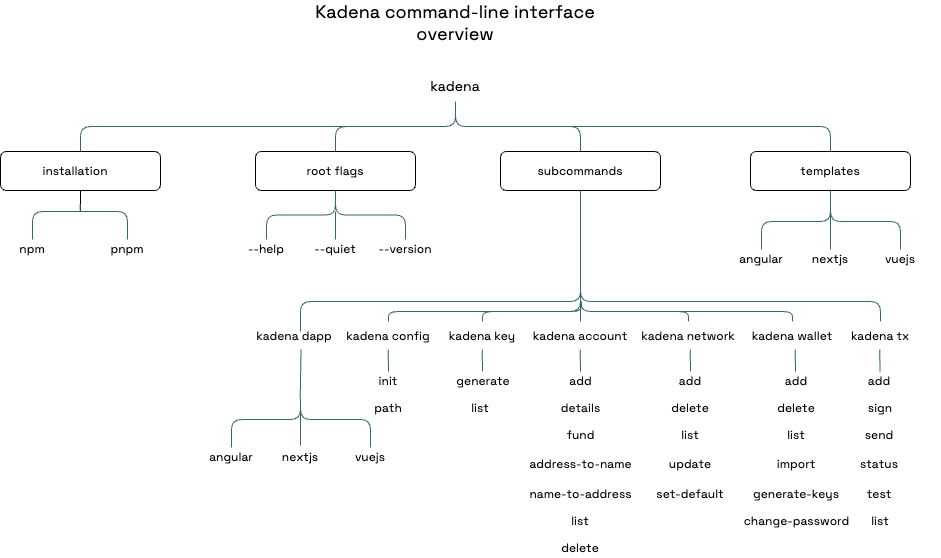
Prepare a development workspace
You can use the kadena entry point to run commands that help you set up a complete local development environment.
You can use the command-line interface to generate random keys, create local wallets, add accounts, customize network connections, and construct and send transactions.
After you prepare a development workspace, you can use kadena CLI commands in combination with other tools—like Pact and Kadena client—to create, test, deploy, and manage decentralized applications for the Kadena network.
Start with interactive prompting
The kadena-cli package is designed to simplify setting up a development environment.
Its intuitive commands prompt you for all of the information required to complete tasks, like creating accounts or managing keys.
Responding to prompts interactively is typically the best approach when getting started, eliminating the need to look up or remember the arguments required for the action you want to perform.
To start using the CLI in interactive Mode, you simply type kadena followed by a subject that describes the type of information you want to work with and a verb to describe what you want to do. You don't need to specify any additional arguments or options.
For example, if you want to add a new wallet but aren't sure of all the required flags and arguments, you can start by entering the following command:
kadena wallet add
The CLI then displays interactive prompts, asking for the information required to successfully complete the task at hand—in this example, adding the wallet to your local development environment. As you gain experience, you can reduce interactive prompting by specifying some or all of the arguments as part of the command. If you run any command without specifying all of its required parameters, the CLI prompts you to provide the missing information.
Configure initial settings
After installing the kadena-cli package, the first step for working with the Kadena command-line interface is to use kadena config init to create a configuration folder to store information about your development environment and connecting to Kadena networks.
Depending on where you want the configuration settings available for your projects to use, you can create the configuration folder in a working directory or in your home directory.
By default, a Kadena configuration folder named .kadena is created in your current working directory.
The settings in the folder are then available to projects within that directory.
For example, if you run kadena config init with $HOME/projects/my-kadena-project as your current working folder, you can access the .kadena
configuration settings from anywhere inside the my-kadena-project project folder.
Creating the configuration folder in a working directory enables you to have different configuration settings for different projects.
If you want to use the same configuration settings from any folder on your computer, you can create a global configuration folder in your home directory by running the kadena config init --global command. The --global command-line option adds the kadena configuration folder to the .config folder in your home directory so that the settings are available globally on your computer.
Configuration settings that are defined in a local working directory take precedence over configuration settings defined in the home directory.
If you add more than one configuration folder to your development environment, you can use kadena config show to see details about the development environment you have configured in your working or global directory.
To configure initial settings:
-
Open a terminal shell on the computer where you've installed the
kadena-clipackage. -
Enter
kadena config initon the command line to create the configuration folder interactively:kadena config initkadena config initThis command creates the
.kadenaconfiguration folder location is your current working directory confirmed and adds default network settings to anetworkssubfolder, then prompts you to create a wallet. For example:Created configuration directory: /Users/pistolas/MY-KADENA/.kadena Added default networks: - mainnet - testnet - devnet ? Would you like to create a wallet? (Use arrow keys) ❯ Yes NoCreated configuration directory: /Users/pistolas/MY-KADENA/.kadena Added default networks: - mainnet - testnet - devnet ? Would you like to create a wallet? (Use arrow keys) ❯ Yes NoIf you already have keys and an account or an existing wallet that you want to use, you can select No to end the interactive session. However, wallets are an important part of interacting with any blockchain, so you can create one now as part of your initial configuration steps.
-
Select Yes and press Return to continue setting up your local development environment.
-
Enter a wallet name and press Return. For example:
? Enter your wallet name: pistolas? Enter your wallet name: pistolas -
Enter and confirm a password for the wallet to generate a public and secret key pair. For example:
? Enter the new wallet password: ********? Re-enter the password: ********? Enter the new wallet password: ********? Re-enter the password: ********After entering the password, you are prompted to create an account using the wallet key generated for your first wallet. For example:
? Create an account using the first wallet key? (Use arrow keys)❯ Yes No? Create an account using the first wallet key? (Use arrow keys)❯ Yes No -
Select Yes to continue setting up your local development environment with a local account.
-
Enter an alias for the local account and press Return. For example:
? Enter an alias for an account: pistolas-kda? Enter an alias for an account: pistolas-kdaThe command automatically creates a local Kadena principal account and displays information about your account and wallet. For example:
====================================================== 🚨 IMPORTANT: Mnemonic Phrase 🚨 ======================================================Mnemonic Phrase:upset crater alien galaxy humble appear prize all glove globe music number Please store the mnemonic phrase in a SAFE and SECURE place. This phrase is the KEY to recover your wallet. Losing it means losing access to your assets. ==================================================== First keypair generatedpublicKey: 61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546 Wallet Storage Location.kadena/wallets/pistolas.yaml Account createdaccountName: k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546 Account Storage Location.kadena/accounts/pistolas-kda.yaml Executed:kadena config init --create-wallet="true" --wallet-name="pistolas" --create-account="true" --account-alias="pistolas-kda"====================================================== 🚨 IMPORTANT: Mnemonic Phrase 🚨 ======================================================Mnemonic Phrase:upset crater alien galaxy humble appear prize all glove globe music number Please store the mnemonic phrase in a SAFE and SECURE place. This phrase is the KEY to recover your wallet. Losing it means losing access to your assets. ==================================================== First keypair generatedpublicKey: 61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546 Wallet Storage Location.kadena/wallets/pistolas.yaml Account createdaccountName: k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546 Account Storage Location.kadena/accounts/pistolas-kda.yaml Executed:kadena config init --create-wallet="true" --wallet-name="pistolas" --create-account="true" --account-alias="pistolas-kda"Be sure to copy and store the mnemonic phrase in a safe place. This 12-word secret phrase is required if you ever need to recover your wallet.
You now have a public key that you can use to sign transactions and authorize certain activity. In this example, the public key for the wallet is 61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546. You also have the principal account associated with the key. In this example, the principal account name is k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546.
For more information about accounts names, keys, and principal accounts, see Accounts, keys, and principals.
View wallet and account information
At this point, you have one public and secret key pair, a local wallet, and a local account. However, this information isn't associated with a specific network—devnet, testnet, or mainnet—or with any chain identifier (0-19). Before you add the account to a specific network and chain, you might want to verify the information you have defined so far to understand the current state of your development environment.
View wallet information
To view information about the wallet:
-
Open a terminal shell on the computer where you've installed the
kadena-clipackage. -
Enter
kadena wallet liston the command line to list wallet information interactively:kadena wallet listkadena wallet listThis command prompts you to select a wallet. For example:
? Select a wallet: (Use arrow keys)❯ All Wallets pistolas? Select a wallet: (Use arrow keys)❯ All Wallets pistolas -
Select All Wallets, then press Return.
If you have only one wallet, you should see output similar to the following:
Wallet: pistolasAlias Index Public key N/A 0 61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546 Executed:kadena wallet list --wallet-name="all"Wallet: pistolasAlias Index Public key N/A 0 61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546 Executed:kadena wallet list --wallet-name="all"
View account information
To view information about the account:
-
Open a terminal shell on the computer where you've installed the
kadena-clipackage. -
Enter
kadena account liston the command line to list account information interactively:kadena account listkadena account listThis command prompts you to select an account. For example:
? Select an account (alias - account name): (Use arrow keys)❯ All accounts pistolas-kda - k:61cf22....6c355546? Select an account (alias - account name): (Use arrow keys)❯ All accounts pistolas-kda - k:61cf22....6c355546 -
Select All accounts, then press Return.
If you have only one account, you should see output similar to the following:
Alias Name Public Key(s) Predicate Fungiblepistolas-kda k:61cf22aa8f20....7743bf6c355546 61cf22aa8f....bf6c355546 keys-all coin Executed:kadena account list --account-alias="all"Alias Name Public Key(s) Predicate Fungiblepistolas-kda k:61cf22aa8f20....7743bf6c355546 61cf22aa8f....bf6c355546 keys-all coin Executed:kadena account list --account-alias="all"Note that the account name k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546, shortened to k:61cf22aa8f20....7743bf6c355546, uses the default keys-all predicate and the fungible for the account is coin. The keys-all predicate is a guard. Guards define the condition that must be satisfied for an operation to proceed. In this case, all public keys associated with the k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546 account must sign transactions.
The first wallet and default account information provide you with the basics for signing transactions: a public key, an account name, and a predicate. However, there aren't many practical applications that involve signing transactions using a local account. Before you can use an account to send and receive funds and sign the most common types of transactions, it must exist on a network and have funds on one or more chains.
Fund your first onchain account
To create an account on the Kadena main network, you need to either have KDA already or know someone who can transfer funds to your account for you.
However, for local development or development on the Kadena test network, you can fund your account using kadena account commands, a faucet application, or publicly available private keys.
If you created a local wallet and an account using the wallet key, you can use that information to add your account to the development or test network on one or more chains.
To fund an onchain account:
-
Open a terminal shell on the computer where you've installed the
kadena-clipackage. -
Enter
kadena account fundon the command line to fund an account interactively:kadena account fundkadena account fund -
Select the account alias you used for your first account. For example:
? Select an account (alias - account name): (Use arrow keys)❯ pistolas-kda - k:61cf22....6c355546? Select an account (alias - account name): (Use arrow keys)❯ pistolas-kda - k:61cf22....6c355546 -
Enter an amount, then press Return.
-
For example:
? Enter an amount: 2? Enter an amount: 2You can request up to 20 coins per network. If you select more than one chain in the request, the coins are distributed equally over the chain identifiers you specify. For example, if you request 20 coins for the development network and chains 0-3, each chain receives five coins.
-
Select a network, then press Return. For example, enter devnet to make this account available on the local development network:
? Select a network: (Use arrow keys)❯ devnet testnet? Select a network: (Use arrow keys)❯ devnet testnet -
Select one or more chain identifiers, then press Return. For example, enter all:
? Enter a ChainId (0-19) (comma or hyphen separated e.g 0,1,2 or 1-5 or all): all? Enter a ChainId (0-19) (comma or hyphen separated e.g 0,1,2 or 1-5 or all): allIf prompted to deploy the faucet module on the network, select Yes. For example:
? Do you wish to deploy faucet module? (Use arrow keys)❯ Yes No? Do you wish to deploy faucet module? (Use arrow keys)❯ Yes NoIf you selected all chains and are deploying the faucet module, you should see output similar to the following:
Deployed faucet module on chain "18, 0, 7, 12, 4, 3, 1, 6, 11, 10, 13, 9, 14, 5, 16, 15, 2, 8, 19, 17" in "devnet" network. Success with Warnings:Account "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" does not exist on Chain ID(s) 3, 8, 6, 11, 1, 16, 5, 10, 2, 4, 9, 13, 0, 7, 18, 19, 15, 12, 14, 17. So the account will be created on these Chain ID(s). Transaction explorer URL for Chain ID "0" : http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/7vkKlYWDDyM8Ceau1gEG_8G6UfwZsahYgsafEd5ak74...Chain ID "19" : http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/JbQ4KlPGxTEfeirvDd7HOj4uwFG8HVipmmNfP4YnmLM✔ Funding account successful. Account "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" funded with 2 coin(s) on Chain ID(s) "0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19" in development network.Use "kadena account details" command to check the balance. Executed:kadena account fund --account="pistolas-kda" --amount="2" --network="devnet" --chain-ids="all" --deployFaucetDeployed faucet module on chain "18, 0, 7, 12, 4, 3, 1, 6, 11, 10, 13, 9, 14, 5, 16, 15, 2, 8, 19, 17" in "devnet" network. Success with Warnings:Account "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" does not exist on Chain ID(s) 3, 8, 6, 11, 1, 16, 5, 10, 2, 4, 9, 13, 0, 7, 18, 19, 15, 12, 14, 17. So the account will be created on these Chain ID(s). Transaction explorer URL for Chain ID "0" : http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/7vkKlYWDDyM8Ceau1gEG_8G6UfwZsahYgsafEd5ak74...Chain ID "19" : http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/JbQ4KlPGxTEfeirvDd7HOj4uwFG8HVipmmNfP4YnmLM✔ Funding account successful. Account "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" funded with 2 coin(s) on Chain ID(s) "0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19" in development network.Use "kadena account details" command to check the balance. Executed:kadena account fund --account="pistolas-kda" --amount="2" --network="devnet" --chain-ids="all" --deployFaucet -
Verify account information for the account for a subset of by chains. For example, to see account details for chains 1, 2, and 3 formatted as JSON output, you can specify command-line options similar to the following:
kadena account details --account="pistolas-kda" --network="devnet" --chain-ids="1-3" --jsonkadena account details --account="pistolas-kda" --network="devnet" --chain-ids="1-3" --jsonThis command displays output similar to the following:
Details of account "pistolas-kda" on network "development"[ { "1": { "guard": { "pred": "keys-all", "keys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ] }, "balance": 2, "account": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" } }, { "2": { "guard": { "pred": "keys-all", "keys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ] }, "balance": 2, "account": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" } }, { "3": { "guard": { "pred": "keys-all", "keys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ] }, "balance": 2, "account": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" } },]Details of account "pistolas-kda" on network "development"[ { "1": { "guard": { "pred": "keys-all", "keys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ] }, "balance": 2, "account": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" } }, { "2": { "guard": { "pred": "keys-all", "keys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ] }, "balance": 2, "account": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" } }, { "3": { "guard": { "pred": "keys-all", "keys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ] }, "balance": 2, "account": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" } },]
You now have one account on the development network with the same account name and public key on twenty development chains. The account on each chain has a balance of two KDA coins. To make this development environment more interesting—and learn about additional CLI commands—you can create additional accounts on the development network or the test network.
Add another account
There are several ways you can create additional accounts for testing in your local development environment. For example, you can:
- Add another wallet with a completely new public and secret key pair (kadena wallet add).
- Generate new random keys for a completely independent account (kadena key generate).
- Import keys from a wallet you've previously created for a new account (kadena wallet import).
- Add new keys from your first wallet to create a new account (kadena account add).
The following example illustrates how to use kadena account add to create a new local account.
To add a new local account:
-
Open a terminal shell on the computer where you've installed the
kadena-clipackage. -
Enter
kadena account addon the command line to fund an account interactively:kadena account addkadena account addYou are prompted to select the method for providing the public keys for the new account. Because you already have a wallet, you can add a new account based on the public key and secret key pair generated for that wallet. If you have other keys you want to use, you can also add accounts by manually providing them. However, to keep things simple, use your first wallet.
-
Use the arrow keys to select Wallet, then press Return. For example:
? How would you like to add the account locally? Manually - Provide public keys to add to account manually❯ Wallet - Provide public keys to add to account by selecting from a wallet? How would you like to add the account locally? Manually - Provide public keys to add to account manually❯ Wallet - Provide public keys to add to account by selecting from a wallet -
Select the wallet alias you set for the first wallet, then press Return. For example:
? Select a wallet: (Use arrow keys)❯ Wallet: pistolas? Select a wallet: (Use arrow keys)❯ Wallet: pistolas -
Enter a new alias for this account, then press Return.
Because you're adding a new account for this wallet, you must give it a new alias. For example:
? Enter an alias for an account: pistolas-local? Enter an alias for an account: pistolas-local -
Enter the name of a fungible for the account, then press Return.
You can specify coin or nft as the fungible for an account. For most accounts, the default—coin—is appropriate. You can press Return to accept the default.
? Enter the name of a fungible: coin? Enter the name of a fungible: coin -
Select the public keys that should be used for the account.
You can select Generate new public key to generate a new random public key from the original wallet key pair. This key can be recovered using the same 12-word secret phrase you saved for your first wallet. For example:
? Select public keys to add to account(index - alias - publickey): ◯ 0 61cf22aa8f....bf6c355546❯◉ Generate new public key? Select public keys to add to account(index - alias - publickey): ◯ 0 61cf22aa8f....bf6c355546❯◉ Generate new public key -
Enter the wallet password, then press Return.
-
Select a keyset predicate for the account, then press Return.
If this account is only going to have one owner and one public key, select the default keys-all predicate. If an account has more than one owner and public key, select an appropriate predicate.
After you select the predicate and press Return, the account information is displayed in a confirmation message similar to the following:
The account configuration "pistolas-local" has been saved in .kadena/accounts/pistolas-local.yaml Executed:kadena account add --from="wallet" --wallet-name="pistolas" --account-alias="pistolas-local" --fungible="coin" --public-keys="ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105" --predicate="keys-all"The account configuration "pistolas-local" has been saved in .kadena/accounts/pistolas-local.yaml Executed:kadena account add --from="wallet" --wallet-name="pistolas" --account-alias="pistolas-local" --fungible="coin" --public-keys="ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105" --predicate="keys-all"
You now have one onchain account and one local account.
View updated account information
After you've added a second account, you might want to check your updated information with a simple command-line option instead of interactive prompting.
To verify your updated account information:
-
Open a terminal shell in your working or home directory.
-
Verify the information for all accounts by running the following command:
kadena account list --account-alias="all"kadena account list --account-alias="all"The command now displays information for two account similar to the following:
Alias Name Public Key(s) Predicate Fungiblepistolas-kda k:61cf22aa8f20....7743bf6c355546 61cf22aa8f....bf6c355546 keys-all coin pistolas-local k:ad833b6bbfc7....28f3249fd5e105 ad833b6bbf....249fd5e105 keys-all coinAlias Name Public Key(s) Predicate Fungiblepistolas-kda k:61cf22aa8f20....7743bf6c355546 61cf22aa8f....bf6c355546 keys-all coin pistolas-local k:ad833b6bbfc7....28f3249fd5e105 ad833b6bbf....249fd5e105 keys-all coin
Format command output
In some cases, you might want to format the output from a command, so it can be used as input to another command or easier to parse.
You can use the --json or --yaml flag to convert the output from virtually any CLI command to JSON or YAML format.
To format the output using JSON:
-
Open a terminal shell in your working or home directory.
-
Add the
--jsonflag to the command line.For example:
kadena account list --account-alias="all" --jsonkadena account list --account-alias="all" --jsonWith the
--jsonflag, the command displays account information in JSON format similar to the following:[ { "name": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546", "fungible": "coin", "publicKeys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ], "predicate": "keys-all", "alias": "pistolas-kda.yaml" }, { "name": "k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105", "fungible": "coin", "publicKeys": [ "ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105" ], "predicate": "keys-all", "alias": "pistolas-local.yaml" }][ { "name": "k:61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546", "fungible": "coin", "publicKeys": [ "61cf22aa8f209b1a5549242601b4a217f034e3d931b6522ccb7743bf6c355546" ], "predicate": "keys-all", "alias": "pistolas-kda.yaml" }, { "name": "k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105", "fungible": "coin", "publicKeys": [ "ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105" ], "predicate": "keys-all", "alias": "pistolas-local.yaml" }]
Add a simple transaction
You must have an onchain account to sign and submit transactions that transfer funds. However, you can use local accounts for transactions that read information from the blockchain or that execute commands with local calls. The following example illustrates how to create and execute a simple transaction using a transaction template and a local account.
Create a transaction template
To create a transaction template:
-
Open a terminal shell in your working or home directory..
-
Create a YAML API request file to execute a simple command similar to the following:
code: (* 5 5)meta: chainId: '{{chain-id}}' sender: '{{{account:from}}}' gasLimit: 600 gasPrice: 0.000001 ttl: 600networkId: '{{network:networkId}}'code: (* 5 5)meta: chainId: '{{chain-id}}' sender: '{{{account:from}}}' gasLimit: 600 gasPrice: 0.000001 ttl: 600networkId: '{{network:networkId}}'This transaction uses template variables to construct a transaction. You can learn more about transaction templates and variables in Construct a transaction and Template prefixes and input values. For more information about using YAML request files for transactions, see Request YAML file format.
-
Save the file as a transaction template by giving it a name with the
.ktplfile extension and moving the file to the.kadena/transaction-templatesfolder.For example, save the file as
.kadena/transaction-templates/simple-code.ktplin your working directory.
Create the transaction
To create a transaction from the template:
-
Create a transaction from the template by running the following command:
kadena tx addkadena tx add -
Select the transaction template you created, then press Return.
For example:
? Which template do you want to use: Select file path safe-transfer.ktpl❯ simple-code.ktpl transfer.ktpl? Which template do you want to use: Select file path safe-transfer.ktpl❯ simple-code.ktpl transfer.ktpl -
Press Return to skip using a data file.
-
Specify any chain identifier, then press Return.
-
Select your local account alias as the transaction sender, then press Return.
For example:
? Select account alias for template value account:from: Enter account manually pistolas-kda k:61cf22....6c355546 coin 61cf2....355546 keys-all❯ pistolas-local k:ad833b....9fd5e105 coin ad833....d5e105 keys-all? Select account alias for template value account:from: Enter account manually pistolas-kda k:61cf22....6c355546 coin 61cf2....355546 keys-all❯ pistolas-local k:ad833b....9fd5e105 coin ad833....d5e105 keys-all -
Select the network for the transaction, then press Return.
? Select network id for template value networkId: (Use arrow keys)❯ devnet mainnet testnet? Select network id for template value networkId: (Use arrow keys)❯ devnet mainnet testnet -
Type a name for the transaction request JSON file, then press Return.
In this example, the transaction request is named
my-code. After you press Return the command displays the JSON object, the location of the file, and the command executed to create the transaction. For example:{ "cmd": "{\"payload\":{\"exec\":{\"code\":\"(* 5 5)\",\"data\":{}}},\"nonce\":\"\",\"networkId\":\"development\",\"meta\":{\"sender\":\"k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105\",\"chainId\":\"3\",\"creationTime\":1715888245,\"gasLimit\":600,\"gasPrice\":0.000001,\"ttl\":600},\"signers\":[]}", "hash": "hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic", "sigs": []} transaction saved to: ./my-code.json Executed:kadena tx add --template="simple-code.ktpl" --template-data="" --chain-id="3" --account:from="k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105" --network:networkId="development" --out-file="my-code.json"{ "cmd": "{\"payload\":{\"exec\":{\"code\":\"(* 5 5)\",\"data\":{}}},\"nonce\":\"\",\"networkId\":\"development\",\"meta\":{\"sender\":\"k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105\",\"chainId\":\"3\",\"creationTime\":1715888245,\"gasLimit\":600,\"gasPrice\":0.000001,\"ttl\":600},\"signers\":[]}", "hash": "hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic", "sigs": []} transaction saved to: ./my-code.json Executed:kadena tx add --template="simple-code.ktpl" --template-data="" --chain-id="3" --account:from="k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105" --network:networkId="development" --out-file="my-code.json"
Test the transaction
To test the transaction:
-
Submit the transaction on the local endpoint by running the following command:
kadena tx testkadena tx test -
Select the transaction you created from the template, then press Return. For example:
? Select a transaction file:❯◉ Transaction: my-code.json? Select a transaction file:❯◉ Transaction: my-code.jsonAfter you press Return, you should see output similar to the following:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- txSignedTransaction test result: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Transaction info: fileName: my-code.json transactionHash: hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic Response: Response: gas: 6 result: status: success data: 25 reqKey: hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic logs: wsATyGqckuIvlm89hhd2j4t6RMkCrcwJe_oeCYr7Th8 metaData: publicMeta: creationTime: 1715888245 ttl: 600 gasLimit: 600 chainId: 3 gasPrice: 0.000001 sender: k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105 blockTime: 1715888557715218 prevBlockHash: Gf_T16uJG4TtVG1VKzIsvHrgbGW4_93mRMucymBeTu8 blockHeight: 4029 continuation: null txId: null Details: chainId: 3 network: devnet networkId: development networkHost: http://localhost:8080 networkExplorerUrl: http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/ Transaction Command: cmd: {"payload":{"exec":{"code":"(* 5 5)","data":{}}},"nonce":"","networkId":"development","meta":{"sender":"k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105","chainId":"3","creationTime":1715888245,"gasLimit":600,"gasPrice":0.000001,"ttl":600},"signers":[]} hash: hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic sigs:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Executed:kadena tx test --tx-signed-transaction-files="my-code.json" --tx-transaction-network="devnet"-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- txSignedTransaction test result: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Transaction info: fileName: my-code.json transactionHash: hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic Response: Response: gas: 6 result: status: success data: 25 reqKey: hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic logs: wsATyGqckuIvlm89hhd2j4t6RMkCrcwJe_oeCYr7Th8 metaData: publicMeta: creationTime: 1715888245 ttl: 600 gasLimit: 600 chainId: 3 gasPrice: 0.000001 sender: k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105 blockTime: 1715888557715218 prevBlockHash: Gf_T16uJG4TtVG1VKzIsvHrgbGW4_93mRMucymBeTu8 blockHeight: 4029 continuation: null txId: null Details: chainId: 3 network: devnet networkId: development networkHost: http://localhost:8080 networkExplorerUrl: http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/ Transaction Command: cmd: {"payload":{"exec":{"code":"(* 5 5)","data":{}}},"nonce":"","networkId":"development","meta":{"sender":"k:ad833b6bbfc72fb7d18b88cd5b4349f82b2f015be8e4b5e7ad28f3249fd5e105","chainId":"3","creationTime":1715888245,"gasLimit":600,"gasPrice":0.000001,"ttl":600},"signers":[]} hash: hyu6NGeQybOGOdJtnuZZ5SJoxurzTyTE2q5yd9OX-ic sigs:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Executed:kadena tx test --tx-signed-transaction-files="my-code.json" --tx-transaction-network="devnet"
Set a default network
Many commands require you to specify the network you want to work with.
You can streamline command execution by setting a default network.
For example, if you are just getting started, you might want to set the default network to devnet to save time as you iterate on your application.
Later, you might want to unset the default, so you can specify the network to use on a command-by-command basis.
As your application matures, you might want change the default network from devnet to testnet so you can deploy updates for broader testing.
To set the default network:
-
Open a terminal shell on the computer where you've installed the
kadena-clipackage. -
Enter
kadena network set-defaulton the command line to set the default network interactively:kadena network set-defaultkadena network set-defaultBecause you're running the command interactively, you are prompted to select a network. For example:
? Select a network (Use arrow keys)❯ devnet mainnet testnet? Select a network (Use arrow keys)❯ devnet mainnet testnet -
Use the up and down arrow keys to select the network you want to use as your default network, then press Return. For example, select devnet, then press Return.
-
Select Yes to confirm your default network, then press Return.
The command displays confirmation of your default network. For example:
The network configuration "devnet" has been set as default. Executed:kadena network set-default --network="devnet" --confirmThe network configuration "devnet" has been set as default. Executed:kadena network set-default --network="devnet" --confirmAfter settings default network, you won't be prompting to select a network when running other commands. If you want to remove the default network from your configuration, run the following command:
kadena network set-default --network none --confirmkadena network set-default --network none --confirmThe command displays confirmation of your change. For example:
The default network configuration has been removed.The default network configuration has been removed.
Run commands in automated scripts
For most commands, responding to interactive prompts and confirmation messages helps to ensure that you provide all of the information necessary to successfully execute each command.
However, if you want to disable all interactive prompts and confirmation messages, you can use the --quiet flag.
The --quiet flag enables you to run commands in environments where interactive input is impractical, such as automated test suites and continuous integration (CI) pipelines.
If you include the --quiet flag in a command, the command suppresses all interactive prompts and skips all confirmation messages, so that each command can run uninterrupted without human intervention.
Running commands using the --quiet flag ensures that automated processes can run smoothly and efficiently, without manual input.
If you use the --quiet flag for a command, you must include all required arguments in the command line.
Create a project
You can use the kadena dappcommand to create a new project directory for the decentralized application you want to build.
This command allows you to create an empty project directory or to create a new project from one of the frontend framework templates that are currently supported.
You can create the new project using templates for the following frontend frameworks:
To create a new project from a template:
-
Open a terminal shell on the computer where you've installed the
kadena-clipackage. -
Enter
kadena dapp create <app-name>on the command line to create a new project directory with the name you specify. For example, to create a project names my-to-do:kadena dapp add my-to-dokadena dapp add my-to-doBecause you're running the command interactively, you are prompted to select a template. For example:
? What template do you want to use? (Use arrow keys)❯ Angular Next JS Vue JS? What template do you want to use? (Use arrow keys)❯ Angular Next JS Vue JS -
Use the up and down arrow keys to select the template to use for your project, then press Return.
If you are missing required dependencies for the template you select, you are prompted to install them.
-
Confirm that you want to install missing dependencies.
-
Change to your project directory by running a command similar to the following:
cd my-to-docd my-to-doIf you explore the project directory, you'll see it contains the appropriate template files and folders for the framework you selected plus a
pactfolder with some starter code for a Pact module (message-store.pact) and for testing the Pact module in the Pact REPL (message-store.repl).
Next steps
Learn more about the Kadena command-line interface and the actions you can perform using CLI commands in the Command-line reference section. To get started with building a smart contract backend for your application, see Smart contracts. For information about using the Kadena client libraries and packages, see Frontend frameworks.